Welcome to our comprehensive guide on creating a TIFF file in ArcGIS. Whether you’re a GIS professional or a novice user, this step-by-step tutorial will walk you through the process of creating high-quality TIFF files for your projects. With ArcGIS’s powerful tools and our easy-to-follow instructions, you’ll be able to achieve professional results effortlessly.
Throughout this guide, we will cover everything you need to know about the process, including downloading and setting up the project package, inspecting the properties of the imagery, improving the symbology of the image, and concluding with the necessary steps to create your TIFF file. By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have the skills and knowledge to apply to other GIS projects and create visually appealing and informative TIFF files.
Key Takeaways:
- Creating a TIFF file in ArcGIS is a straightforward process when following our step-by-step guide.
- Downloading and setting up the project package is essential to ensure you have all the necessary resources for the tutorial.
- Inspecting the properties of the imagery helps optimize its appearance and understand its characteristics.
- Improving the symbology of the image enhances its visualization and creates a more visually appealing TIFF file.
- By following this guide, you can apply your newfound knowledge to other GIS projects and create high-quality TIFF files.
Download and Set Up the Project Package
To begin creating your TIFF file in ArcGIS, you’ll first need to download and set up the project package. This package contains all the necessary files and resources that you’ll be using throughout the tutorial. Follow the instructions below to get started:
- Go to the official ArcGIS Pro website and navigate to the downloads section.
- Choose the appropriate version of ArcGIS Pro for your operating system and click on the download button.
- Once the download is complete, open the installation file and follow the on-screen prompts to install ArcGIS Pro on your computer.
- After the installation is finished, launch ArcGIS Pro and create a new project.
- Within the new project, locate and import the project package that you downloaded earlier.
- Once the project package is imported, you’ll have access to all the necessary data and resources for creating your TIFF file.
By downloading and setting up the project package, you’ll ensure that you have everything you need to proceed with the tutorial smoothly. This will include any additional datasets, symbology files, or geoprocessing tools that are required.
Download and Set Up the Project Package
| Steps | Instructions |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Go to the official ArcGIS Pro website and navigate to the downloads section. |
| Step 2 | Choose the appropriate version of ArcGIS Pro for your operating system and click on the download button. |
| Step 3 | Once the download is complete, open the installation file and follow the on-screen prompts to install ArcGIS Pro on your computer. |
| Step 4 | After the installation is finished, launch ArcGIS Pro and create a new project. |
| Step 5 | Within the new project, locate and import the project package that you downloaded earlier. |
| Step 6 | Once the project package is imported, you’ll have access to all the necessary data and resources for creating your TIFF file. |
Following these steps will ensure that you are ready to proceed with the tutorial and create your TIFF file in ArcGIS. The project package provides a streamlined and organized approach to accessing the required resources, saving you time and effort in gathering the necessary files manually. Let’s move on to the next section to inspect the properties of the imagery dataset that you’ll be working with.
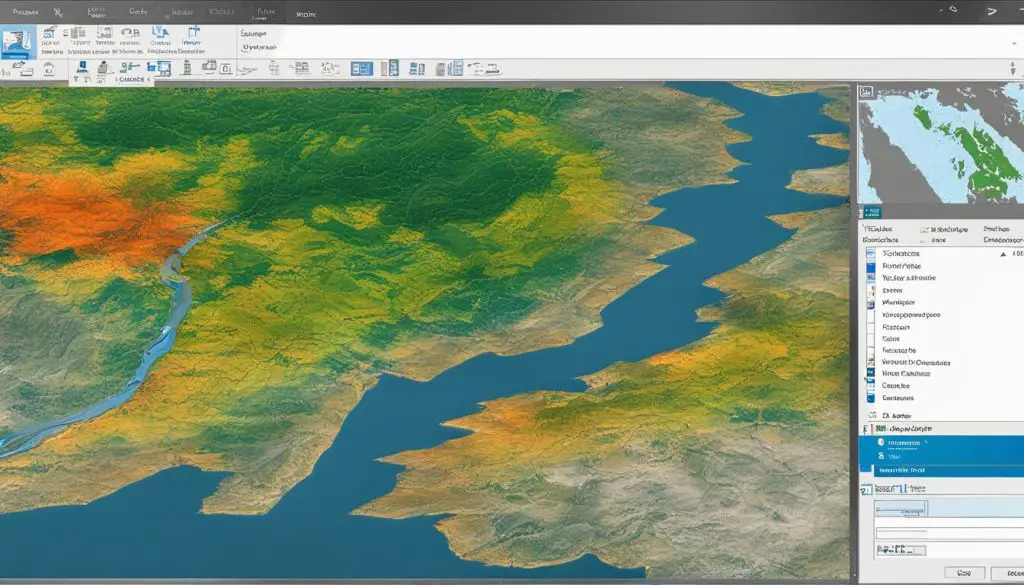
Inspect the Properties of the Imagery
Once you have the project package set up, it’s important to inspect the properties of the imagery dataset that you will be working with. This step will provide valuable information about the characteristics of the data and help you optimize its appearance in ArcGIS Pro. To begin, open the project in ArcGIS Pro and locate the imagery dataset in the Contents pane.
Next, right-click on the dataset and select “Properties” from the context menu. This will open the Layer Properties dialog box, where you can access various tabs containing information about the imagery. The “General” tab will provide an overview of the dataset, including the source, data type, and spatial reference.
Switch to the “Source” tab to review detailed information about the source of the imagery, such as the acquisition date, sensor type, and resolution. This information can be useful for understanding the quality and accuracy of the data. Additionally, you can explore the “Display” tab to adjust the brightness, contrast, and transparency of the imagery to optimize its visualization.
Table 1: Imagery Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Legend | Yes |
| Source Information | Acquisition date: October 10, 2022 Sensor type: Aerial Resolution: 0.5 meters |
| Spatial Reference | Projected coordinate system: WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_10N Geographic coordinate system: GCS_WGS_1984 |
By inspecting the properties of the imagery, you can gain insights into its characteristics and make informed decisions about how to process and analyze it. Understanding the source information, spatial reference, and other properties will help you effectively utilize the imagery for your GIS projects.
Improve the Symbology of the Image
In this section, we will explore how to enhance the symbology of the raster image in order to create a visually appealing and informative TIFF file in ArcGIS. By adjusting the rendering parameters and experimenting with different stretch types and band combinations, you can optimize the visualization of your GIS data.
To begin, zoom in on a specific area of the map that you want to focus on. This will allow you to analyze the details and characteristics of the imagery more effectively. Once you have selected the desired area, proceed to adjust the rendering parameters.
In ArcGIS, you can modify the color ramp, contrast, transparency, and other visual attributes to enhance the appearance of the raster image. Experiment with different settings to find the combination that best represents the features and patterns you want to highlight. Remember to consider the purpose of your TIFF file and the intended audience when choosing the symbology.
Comparing different stretch types and band combinations can also provide valuable insights into your GIS data. By analyzing the variations in color, brightness, and contrast, you can identify patterns, relationships, and anomalies in the imagery. Consider creating a table to summarize the results of your analysis and showcase the differences between the various symbology options.
Conclusion
In conclusion, creating a TIFF file in ArcGIS is a straightforward process that can greatly enhance your GIS projects. By following the step-by-step guide provided in this tutorial, you have learned how to download and set up the necessary project package, inspect the properties of the imagery dataset, and improve the symbology of the image for better visualization.
With your newfound knowledge, you can now apply these techniques to other GIS projects and create high-quality TIFF files for analysis, sharing, and presentation purposes. Remember to save your project and explore other capabilities of ArcGIS Pro for further data analysis and visualization.
By utilizing ArcGIS’s powerful tools and features, you can unlock the full potential of your spatial data and create visually appealing and informative TIFF files. Whether you’re a GIS professional or a beginner, this tutorial provides you with the foundation to create impressive TIFF files that meet your project requirements.
