Photoshop is a powerful image-editing application that supports various image formats, including TIFF. Converting a file into a TIFF format in Photoshop is a simple process that provides versatility and compatibility with a wide range of image-editing applications.
TIFF, or Tagged Image File Format, is a flexible raster image format that is widely supported by image-editing applications. It supports CMYK, RGB, and grayscale images, making it a good option when you need to preserve the quality and details of your image during the conversion process.
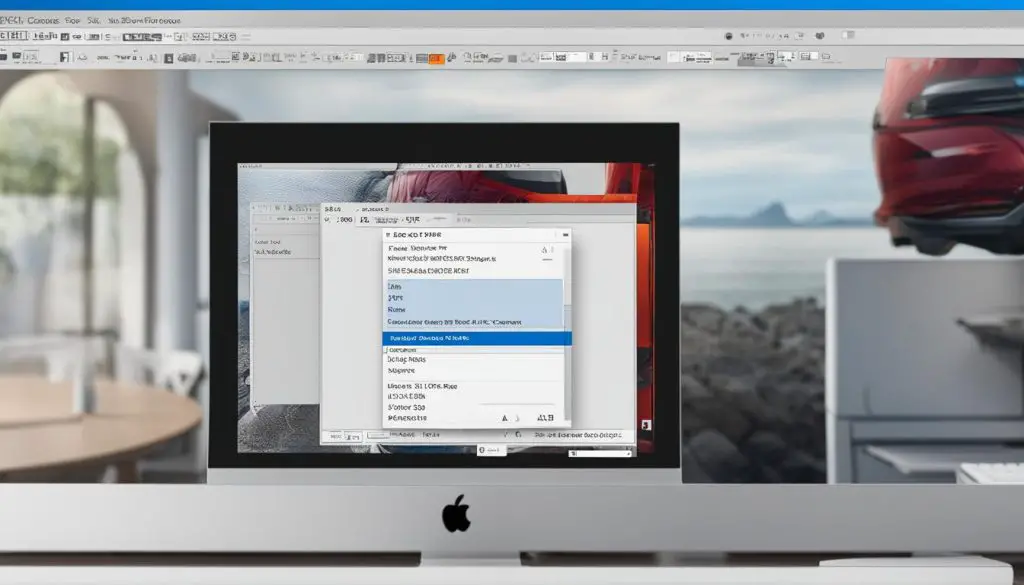
Now let’s dive into the step-by-step process of converting a file into a TIFF format in Photoshop:
Key Takeaways:
- Photoshop supports TIFF, a flexible raster image format.
- TIFF is a good option for preserving image quality and details during the conversion process.
- To convert a file to TIFF in Photoshop, use the “Save As” command.
- TIFF supports CMYK, RGB, and grayscale images.
- Experiment with different image formats supported by Photoshop to find the best option for your specific needs.
Saving JPEGs in Photoshop
In Photoshop, you can easily save your CMYK, RGB, and grayscale images as JPEGs using the “Save As” command. JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) is a commonly used image format that offers high compression while maintaining a good level of image quality. This makes it ideal for sharing images on the web or via email.
When saving an image as a JPEG, Photoshop gives you the option to adjust the quality level. Higher quality levels result in larger file sizes but retain more image detail, while lower quality levels reduce file size but may compromise image clarity. It’s important to find the right balance between file size and image quality depending on your specific needs.
One thing to keep in mind when saving JPEGs in Photoshop is that the format only supports 8-bit images. If you try to save a 16-bit image as a JPEG, Photoshop will automatically convert it to 8-bit. Therefore, it’s advisable to work with 8-bit images or convert your image to 8-bit before saving as a JPEG to ensure compatibility.
“JPEG compression is a convenient way to reduce file sizes while maintaining good image quality. Just remember to choose an appropriate quality level and consider the bit depth of your image to ensure optimal results.”
Comparison of JPEG and TIFF Formats
| JPEG | TIFF | |
|---|---|---|
| Compression | Lossy compression, reduces file size by discarding data | Lossless compression, preserves all image data |
| Bit Depth Support | 8-bit only | Supports CMYK, RGB, and grayscale images in various bit depths |
| File Size | Smaller file size compared to TIFF | Larger file size compared to JPEG |
| Image Quality | Quality can be adjusted with some loss of detail | Preserves high image quality and detail |
| Usage | Ideal for web sharing and emails | Recommended for professional printing and archiving |
As shown in the comparison table above, JPEG and TIFF formats have different characteristics and usage scenarios. While JPEG is widely used for web sharing and emails due to its smaller file size, TIFF offers higher image quality and supports a wider range of color modes and bit depths, making it suitable for professional printing and archiving.
Exporting Images as PNG in Photoshop
When it comes to saving your images in Photoshop, you have various options to choose from. One popular format is PNG, which stands for Portable Network Graphics. This format is widely used for web graphics and supports transparency, making it ideal for images with complex backgrounds or for creating logos and icons.
To export your images as PNG in Photoshop, you can use the “Save As” command. Simply go to the “File” menu, select “Save As,” and choose PNG from the format options. You can then specify the destination folder and file name for your exported image.
It’s worth mentioning that Photoshop also offers additional options for exporting specific items as PNG, such as artboards, layers, and layer groups. You can use the Quick Export or Export As options to choose the desired format (PNG), and Photoshop will automatically export the selected items as separate PNG files.
Table: Exporting Images as PNG in Photoshop
| Action | Shortcut |
|---|---|
| Go to “File” menu | Alt + F |
| Select “Save As” | S |
| Choose PNG from format options | P |
| Specify destination folder and file name | Enter |
By using the export options in Photoshop, you have full control over the quality and other settings of your PNG images. This allows you to fine-tune the output based on your specific requirements. Whether you’re creating web graphics, designing logos, or working on other projects, exporting images as PNG in Photoshop ensures that you can achieve the desired results with ease.
Creating Animated GIFs in Photoshop
Photoshop allows you to unleash your creativity by transforming individual frames into animated GIFs. Whether you want to create a simple animation or showcase a series of images in a loop, Photoshop provides you with the tools to bring your ideas to life. In this section, we will explore the easy steps to turn a file into a TIFF using Photoshop.
First, open your Photoshop document and ensure that it contains the frames you want to include in your animated GIF. To do this, go to the “Window” menu and select “Timeline” to open the timeline panel. From the timeline panel, you can create, duplicate, and delete frames according to your desired animation sequence.
Once you have finalized your animation, go to the “File” menu and select “Save As”. Choose the location on your computer where you want to save the animated GIF, provide a name for the file, and select “GIF” from the “Format” drop-down menu. Finally, click “Save” to save your animated GIF.
By following these quick steps, you can easily create animated GIFs in Photoshop, allowing you to add an extra touch of dynamism and visual appeal to your designs or projects. Now that you know how to turn a file into a TIFF using Photoshop, you can explore the endless possibilities of animation.
Table: Comparing TIFF, JPEG, PNG, and GIF Formats
| Format | Compression | Color Support | Transparency |
|---|---|---|---|
| TIFF | No compression or lossless compression | CMYK, RGB, and grayscale | No transparency support |
| JPEG | Lossy compression | CMYK, RGB, and grayscale | No transparency support |
| PNG | No compression or lossless compression | RGB, Indexed Color, Grayscale, and Bitmap | Supports transparency |
| GIF | No compression or lossless compression | Indexed Color | Supports transparency |
Other Image Formats Supported by Photoshop
In addition to TIFF, Photoshop supports various other image formats. These formats offer different specifications and compatibility with different applications. Here are some of the image formats supported by Photoshop:
EPS (Encapsulated PostScript)
EPS is a widely supported format that is compatible with page-layout, word-processing, and graphics applications. It is commonly used for printing and publishing purposes. EPS files can contain both raster and vector data, making them versatile for different design needs.
BMP (Windows image format)
BMP is a native image format for the Windows operating system. It supports uncompressed raster images and is commonly used for simple graphics and icons. BMP files can be opened and edited in many image-editing applications, including Photoshop.
Cineon
The Cineon format was developed by Kodak for the Cineon Film System, which was used for digital film scanning and processing. It supports high-bit-depth images and is commonly used in the film industry. Photoshop allows you to work with Cineon files, making it a valuable tool for professionals in the film and video production industry.
Targa (TGA) format
The Targa format, also known as TGA, is a raster image format that supports uncompressed images with various color depths. It is commonly used for video game graphics and is supported by many image-editing applications, including Photoshop. TGA files can preserve transparency and are suitable for projects that require high-quality images with alpha channels.
These are just a few examples of the image formats supported by Photoshop. Each format has its own unique features and usage scenarios. By understanding the capabilities of different image formats, you can choose the most suitable format for your specific needs and ensure compatibility across various applications.
Conclusion
Converting a file into a TIFF format in Photoshop is a straightforward process that offers versatility and compatibility with various image-editing applications. By following the easy steps outlined in this Photoshop tutorial for converting files to TIFF, you can save your files in the desired format while preserving the quality and details of your images.
Whether you need to convert a file to TIFF for professional or personal purposes, Photoshop provides a quick guide to turn files into TIFF using its intuitive interface. With support for different image formats, such as CMYK, RGB, and grayscale, Photoshop ensures that your converted TIFF files meet your specific requirements.
Transforming a file into TIFF format in Photoshop can be especially useful when you need to maintain the high quality of your images during the conversion process. TIFF files are widely supported by image-editing applications, making them an ideal choice for professionals working in various industries.
As you explore the various formats supported by Photoshop, consider the unique specifications and usage scenarios of each format. Whether it’s TIFF, JPEG, PNG, or other formats like EPS or BMP, Photoshop provides a comprehensive set of tools to cater to your image conversion needs.
